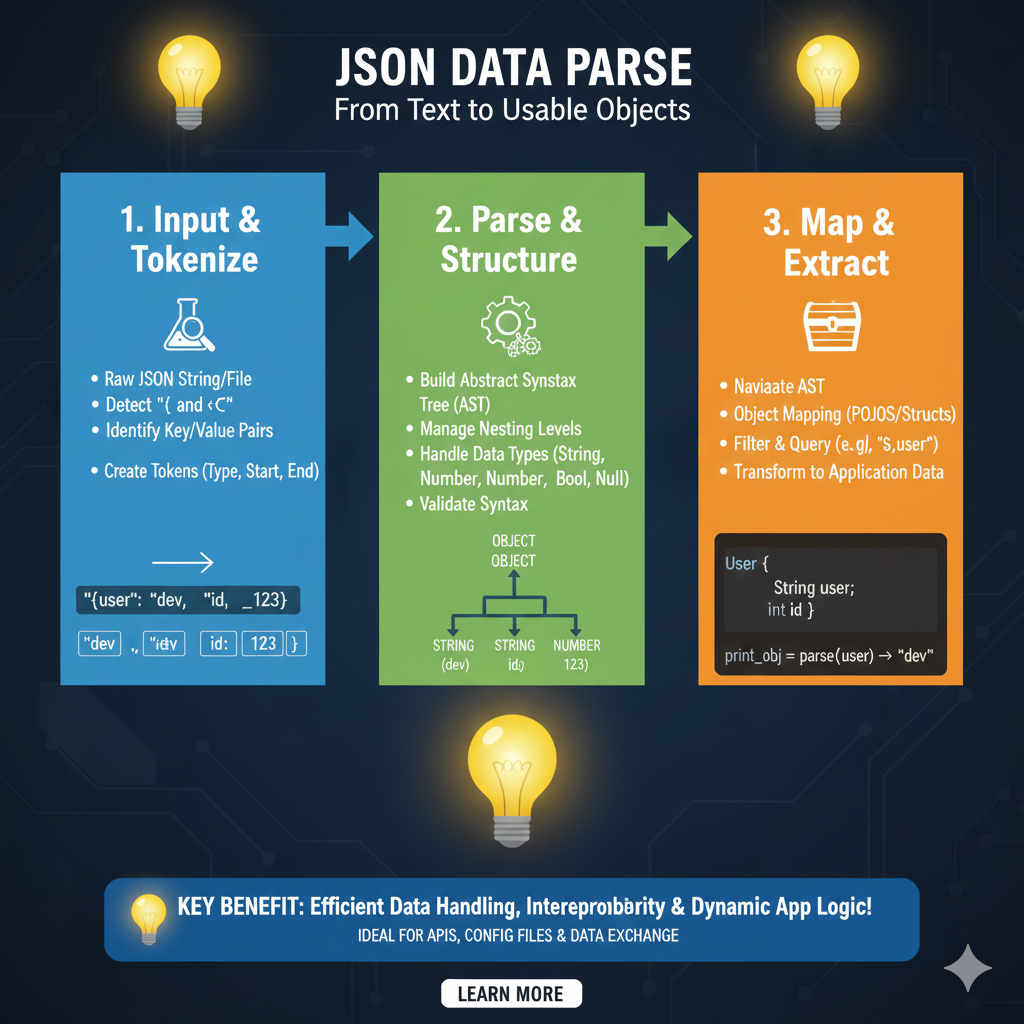
How to Parse JSON in Chrome: A Comprehensive Guide
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) has become the ubiquitous standard for exchanging data between a server and a web application. As a developer, or even just someone frequently interacting with APIs, you’ll often encounter raw JSON data in your browser. While Chrome offers basic viewing capabilities, knowing how to effectively parse and format JSON can significantly boost your productivity and understanding.
Understanding Chrome’s Built-in JSON Viewer
Chrome comes with a basic, yet functional, built-in JSON viewer. When you navigate to a URL that serves raw JSON (e.g., an API endpoint), Chrome will automatically try to display it in a human-readable format. Here’s how it generally works:
- If the server sends the
Content-Type: application/jsonheader, Chrome will automatically format the JSON. - You can click on the arrows (triangles) next to objects and arrays to expand or collapse them, allowing you to navigate through complex structures.
- However, this built-in viewer is quite minimalistic, offering no search or advanced formatting options.
Example of raw JSON (unformatted):
{"id":1,"name":"Alice","email":"alice@example.com","hobbies":["reading","coding"]}Example of raw JSON (formatted by Chrome’s native viewer):
{ "id": 1, "name": "Alice", "email": "alice@example.com", "hobbies": [ "reading", "coding" ]}Boosting Your JSON Parsing with Chrome Extensions
For a richer experience, dedicated Chrome extensions are indispensable. They offer features like syntax highlighting, collapsible sections, search, and even tree views. Here are a couple of popular choices:
JSON Formatter (by callum locke)
This is one of the most widely used and highly-rated JSON formatters. It automatically detects JSON responses and displays them in a beautifully formatted, collapsible tree view.
How to Use JSON Formatter:
- Go to the Chrome Web Store and search for “JSON Formatter”.
- Click “Add to Chrome” and then “Add extension”.
- Once installed, simply open any URL that returns JSON. The extension will automatically take over and display the data in a much more organized way than Chrome’s default viewer.
- You’ll notice features like syntax highlighting, line numbers, and the ability to expand/collapse nodes with ease.
JSON Viewer Pro
Another powerful option, JSON Viewer Pro offers similar features to JSON Formatter but often includes additional functionalities like dark mode, custom themes, and filtering capabilities.
How to Use JSON Viewer Pro:
- Find “JSON Viewer Pro” in the Chrome Web Store.
- Install the extension.
- Navigate to a JSON URL. JSON Viewer Pro will automatically format the output.
- Explore its options, usually accessible via its icon in the Chrome toolbar, to customize the viewing experience.
Why Use a JSON Parser Extension?
- Readability: Converts minified or unformatted JSON into a clean, hierarchical structure.
- Navigation: Easily expand and collapse objects/arrays to focus on specific data points.
- Search: Quickly find specific keys or values within large JSON payloads.
- Validation: Some extensions can highlight syntax errors, helping you debug malformed JSON.
- Copying: Often provides options to copy specific paths or the entire formatted JSON.
Conclusion
While Chrome’s native JSON viewing capabilities are a good starting point, leveraging powerful extensions like JSON Formatter or JSON Viewer Pro can drastically improve your workflow when dealing with JSON data. By understanding “how to” effectively parse JSON in Chrome, you save time, reduce errors, and gain better insights into the data you’re working with. Happy parsing!
Mastering Web-Based JSON Debugging
This technical guide is divided into three functional pillars: core visual features, interactive navigation elements, and advanced professional workflows.
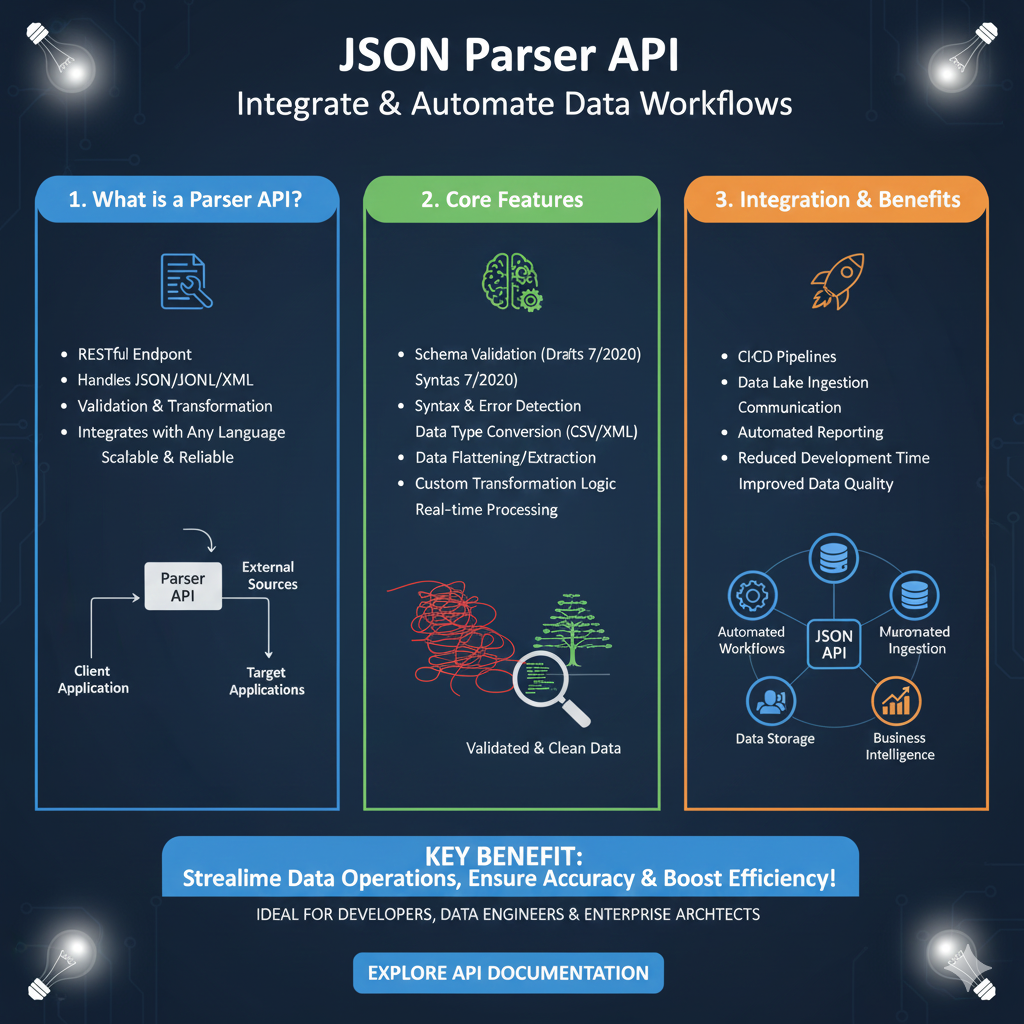
1. Core Features (Blue)
This module focuses on the immediate visual improvements provided by a high-quality browser parser:
- Prettification: Includes Simulated Prettification to turn minified strings into readable, indented structures.
- Visual Clarity: Features Automatic Highlighting for different data types and multiple Visual Themes, specifically including a Dark Mode.
- Deep Navigation: Uses Breadcrumbs & Paths to help developers track their current location within deeply nested objects.
- UI Overview: Displays a browser-based code editor with a theme toggle and syntax-colored key-value pairs.
2. Interactive Navigation (Green)
This section details the tools used to traverse and manipulate large datasets efficiently:
- Collapsible Trees: Provides a clear visual hierarchy with nodes that can be expanded or collapsed to focus on specific data segments.
- Content Previews: Includes image icons to indicate where URL strings resolve to visual assets.
- Searchable Structure: Displays a detailed tree map that organizes data keys into a searchable, interactive interface.
3. Developer Workflow (Orange)
The final pillar explores the integration of parsing tools into the broader development and testing lifecycle:
- Error Management: Built-in Validation & Error Detection to catch syntax issues instantly.
- Data Portability: Supports Schema & Export (CSV) functions to move data between different platforms and tools.
- Console Power: Features Console Integration, allowing developers to interact with parsed JSON objects directly through the browser’s developer tools.
- Integrated Testing: Mentions compatibility with tools like Mock Service Worker for a complete debugging environment.

learn for more knowledge
Mykeywordrank-> Search for SEO: The Ultimate Guide to Keyword Research and SEO Site Checkup – keyword rank checker
json web token->jwt react Authentication: How to Secure Your react app with jwt authentication – json web token
Json Compare ->compare json online free: Master json compare online with the Best json compare tool and online json Resources – online json comparator
Fake Json –>fake api jwt json server: Create a free fake rest api with jwt authentication – fake api