Understanding JSON Parsing in Express.js
When building robust APIs with Node.js and the Express module (or Express.js), you often need to handle incoming data from client applications. A very common format for this data exchange is JSON (JavaScript Object Notation).
However, by default, Express.js does not automatically parse the JSON payload from the request body. If you try to access the req.body property without a proper parser, it will likely be undefined. This is where the powerful express.json() middleware comes into play.
The Evolution: From body-parser to express.json()
The express.json() parser is a built-in middleware function in Express.js (since version 4.16.0). Prior to this, developers had to install the separate body-parser package to get the same functionality.
- express.json(): The modern, built-in solution for Node.js APIs.
- express body-parser (bodyParser.json()): The older, external body parser package. While it still works, express.json() is recommended as it’s built into the Express module, reducing external dependencies.
What is express.json()?
express.json() is a built-in middleware function in Express.js. It parses incoming request bodies with JSON payloads and is based on the body-parser module. It places the parsed JSON data as a JavaScript object on req.body, making the body property easily accessible in your route handlers.
How to Use express.json() (The Parser Middleware)
Integrating express.json() into your Node.js application is straightforward. You typically apply this parser middleware globally using app.use() before your route definitions, ensuring that all incoming requests with a Content-Type: application/json header can benefit from JSON parsing.
JavaScript
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const PORT = 3000;
// Use express.json() middleware to parse JSON request bodies (The JSON Parser)
app.use(express.json());
// A simple POST route to receive JSON data
app.post('/api/data', (req, res) => {
// The parsed JSON data is now accessible on req.body
console.log('Received data:', req.body);
if (req.body && Object.keys(req.body).length > 0) {
res.status(200).json({
message: 'Data received successfully!',
yourData: req.body // Accessing the parsed body property
});
} else {
res.status(400).json({ message: 'No data provided or invalid JSON.' });
}
});
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server running on http://localhost:${PORT}`);
});
This demonstrates the core process of using the express json body parser to handle POST requests.
Configuration Options for express.json()
The express.json() parser middleware accepts an optional options object that allows for customization:
limit: Controls the maximum request body size (default: ‘100kb’). Setting a limit is a security best practice.strict: When true (default), only JSON arrays and objects are accepted.type: Controls the Content-Type header that the middleware will parse (default: ‘application/json’).
JavaScript
// Example with options
app.use(express.json({
limit: '5mb', // Accept up to 5MB of JSON data
strict: true,
type: 'application/json' // Only parse standard JSON
}));
Best Practices and Common Pitfalls
- Middleware Order: Always place app.use(express.json()); before your route handlers that need to consume JSON data. This ensures the req.body property is populated before the handler runs.
- Error Handling for Malformed JSON: If the incoming JSON is malformed (raw JSON string syntax error), the express.json() parser will throw a synchronous error. You must set up a global error handling middleware function to gracefully catch these 400 Bad Request errors:JavaScript
app.use((err, req, res, next) => { // Check for the specific error thrown by express.json() if (err instanceof SyntaxError && err.status === 400 && 'body' in err) { console.error('Bad JSON Payload:', err.message); // Send a clean 400 response return res.status(400).json({ message: 'Invalid JSON payload provided.' }); } next(err); // Pass other errors down the line });- Content-Type Header: Express.json() only activates if the client request sets the Content-Type header to application/json. Without it, the middleware will skip, and req.body will be undefined.
Conclusion
The express.json() middleware function is an indispensable tool for any Express.js developer building APIs in Node.js that consume JSON data. By understanding how to implement this express json parser, its configuration options, and robust error handling, you can ensure your applications efficiently and reliably parse incoming JSON payloads, making the req body readily available for processing.
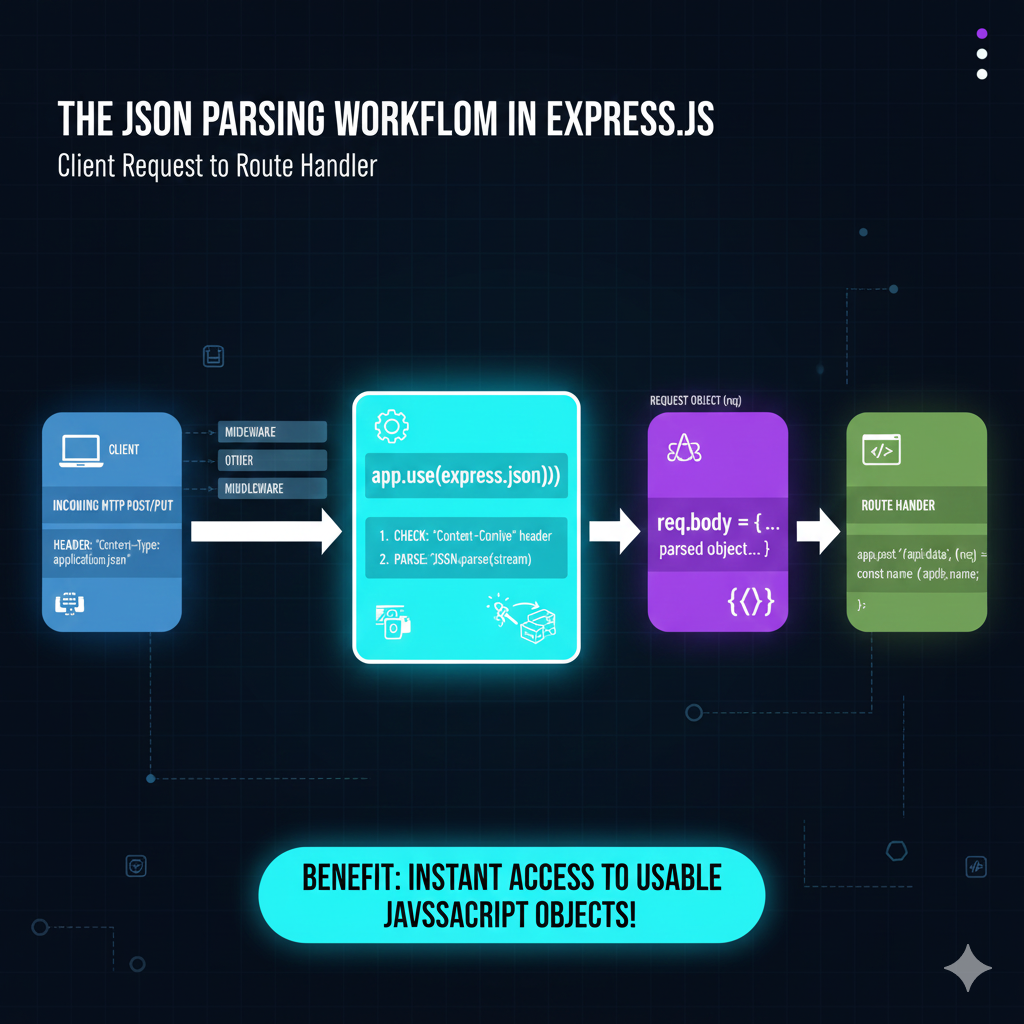
The JSON Parsing Workflow in Express.js
The workflow is broken down into four distinct stages:
1. Incoming Request (Client)
- The process begins with the CLIENT sending an INCOMING HTTP POST/PUT request.
- The request header must contain the crucial signal:
HEADER: "Content-Type: application/json". - The raw data arrives as a binary stream/buffer.
2. The Middleware Action
- Before hitting the route handler, the request passes through the middleware stack, including
app.use(express.json()). - The middleware performs two core steps:
- CHECK: It verifies the
Content-Typeheader. - PARSE: It executes
JSON.parse(stream)to convert the raw JSON string/stream into a structured JavaScript object.
- CHECK: It verifies the
3. Request Object Transformation
- The newly parsed JavaScript object is attached to the REQUEST OBJECT (
req). - Specifically, the parsed object is assigned to
req.body = {...}.
4. Route Handler (Consumption)
- The request finally reaches the ROUTE HANDLER (e.g.,
app.post('/api/data', (req, res) => {...})). - The handler can now directly and easily access the data using dot notation, for example:
const name = req.body.name.
learn for more knowledge
Mykeywordrank-> Search Optimization SEO: Master Search Engine Optimization for Top Rankings – keyword rank checker
Json web token ->How to Use token jwt (JSON Web Tokens) for Secure Authentication – json web token
Json Compare ->Compare JSON File Online: Your Essential JSON Diff and Format Guide – online json comparator
Fake Json –>How to Create Fake JSON API for Faster Development and Testing – fake api
Leave a Reply