JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) has become the de-facto standard for data interchange on the web. As a C developer, you’ll frequently encounter scenarios where you need to json parse or parsing json data, whether it’s from a web API or a configuration file.
While C doesn’t have built-in support for JSON, several robust and efficient third-party json parsers and json libraries make parsing JSON in C straightforward. This guide will walk you through the process, focusing on two of the most popular and reliable libraries: cJSON and Jansson, and briefly touching on yyjson.
Why Use a C JSON Parser Library?
Attempting to json parse manually in C is complex. JSON has a strict json format with nested objects, arrays, various data types, and escape sequences. Writing a parser from scratch would be complex, error-prone, and time-consuming. JSON libraries handle these intricacies for you, providing an elegant API to deserialize JSON strings into C data structures and access their values.
Getting Started with cJSON: The Lightweight JSON Parser
cJSON is a widely used, ultra-lightweight, and easy-to-integrate c json parser and printer for C. It’s known for its simplicity and small footprint, making it ideal for embedded systems or projects where resource usage is critical.
1. Installation and Setup
The cjson library is typically integrated by adding its cJSON.h and cJSON.c files directly to your project. You can download them from the cJSON GitHub repository.
Compile your project along with cJSON.c using your compiler (e.g., gcc your_program.c cJSON.c -o your_program). For larger projects, integrating with cmake is often preferred.
2. Basic JSON Parsing with cJSON
Let’s consider a simple JSON string and json parse it using cJSON:
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "cJSON.h"
int main() {
const char *json_string = "{\"name\":\"John Doe\",\"age\":30,\"isStudent\":false,\"grades\":[85,92,78]}";
cJSON *root = cJSON_Parse(json_string); // Returns a cJSON object
if (root == NULL) {
// Error handling code
return 1;
}
// Accessing values
cJSON *name = cJSON_GetObjectItemCaseSensitive(root, "name");
if (cJSON_IsString(name) && (name->valuestring != NULL)) {
printf("Name: %s\n", name->valuestring); // Accesses valuestring
}
cJSON *age = cJSON_GetObjectItemCaseSensitive(root, "age");
if (cJSON_IsNumber(age)) {
printf("Age: %d\n", age->valueint); // Accesses the number value
}
// Clean up
cJSON_Delete(root); // Always use cJSON_Delete to free memory
return 0;
}
3. Key cJSON Functions Explained:
cJSON_Parse(const char *value): Parses the JSON string and returns a pointer to the root cjson object.cJSON_GetObjectItemCaseSensitive(const cJSON * const object, const char * const string): Retrieves an item from a json object by its key.item->valuestring,item->valueint,item->valuedouble: Accesses the raw value of the JSON item (string, number, etc.).cJSON_Delete(cJSON *item): Frees all memory associated with a cJSON object.
Parsing JSON with Jansson and Other C JSON Parsers (yyjson)
Jansson is another excellent C library for encoding, decoding, and manipulating JSON data. It offers a more robust and feature-rich API compared to cJSON.
A notable modern addition to C json parsers is yyjson. yyjson is known for its extremely fast parsing speed and lightweight design, making it a strong alternative to cJSON for performance-critical tasks.
1. Jansson Installation
Jansson is typically installed via your system’s package manager or compiled from source, often integrated into the build process using cmake. You must link against the json library (e.g., gcc your_program.c -o your_program -ljansson).
2. Jansson Functions
json_loads(const char *input, size_t flags, json_error_t *error): The primary function for json parse.json_object_get(const json_t *object, const char *key): Retrieves a data object by its key.json_decref(json_t *json): Frees the memory using reference counting.
Conclusion: Choosing Your C JSON Parser
Parsing JSON in C doesn’t have to be a headache. By leveraging powerful and well-maintained json libraries like cJSON or Jansson (or modern high-performance options like yyjson), you can efficiently handle JSON data in your C applications.
- cJSON: Choose this for its ultra-lightweight footprint and easy integration (just two files), ideal for embedded or simple parsing json tasks.
- Jansson: Choose this for its robust features, reference counting memory management, and use in larger applications.
- yyjson: Choose this for maximum speed and performance when parsing massive amounts of JSON data.
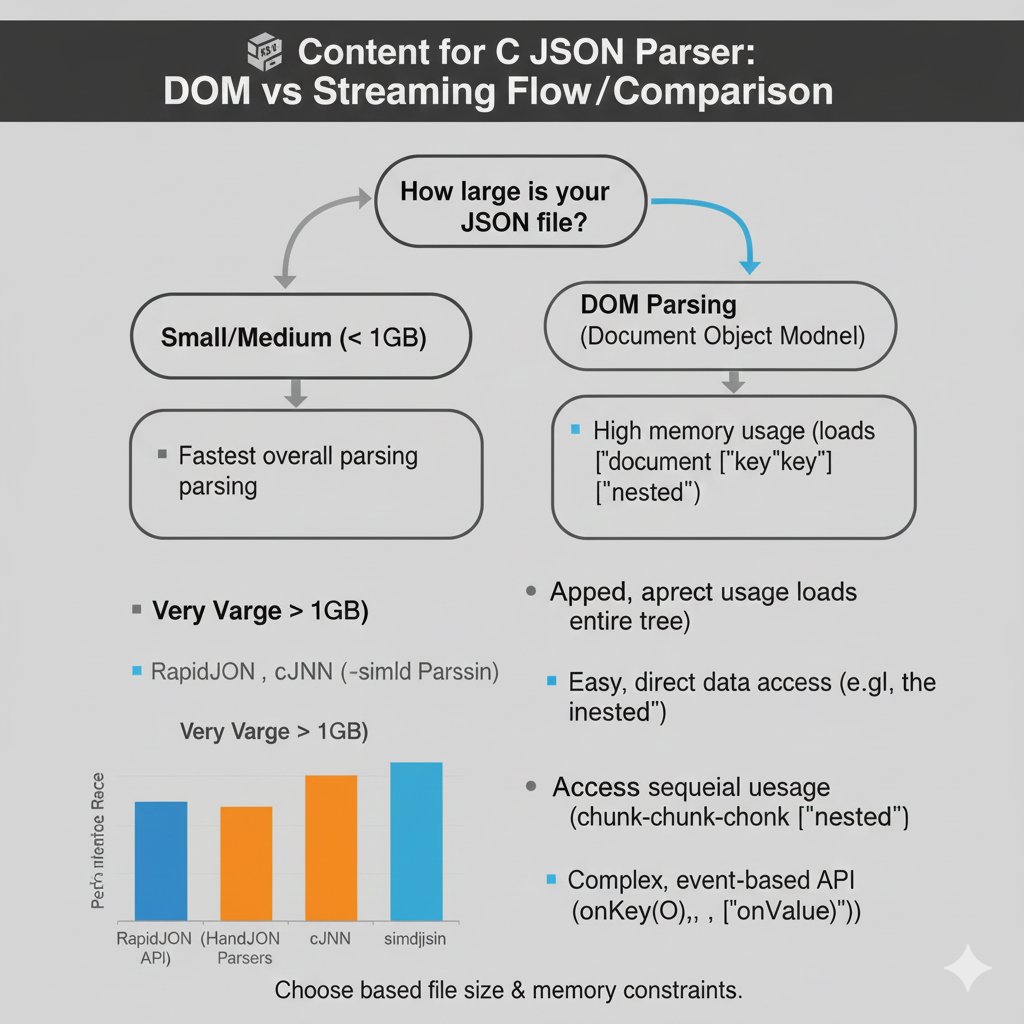
C JSON Parser: DOM vs Streaming
This infographic compares the two main JSON parsing architectures—DOM Parsing and Streaming Parsing—and includes a performance metric visualization for popular C/C++ libraries.
1. Decision Point: File Size
The chart begins with the central question: “How large is your JSON file?”.
| Scenario | Recommended Approach |
| Small/Medium (< 1GB) | Use DOM Parsing (Document Object Model). |
| Very Varge > 1GB | Use Streaming Parsing (Implied, as DOM parsing is memory-intensive for large files). |
2. Comparison of Parsing Methods
| Feature | DOM Parsing (Document Object Model) | Streaming Parsing (Implied) |
| Speed/Parsing | Fastest overall parsing. | N/A (Generally slower than DOM but better for large files). |
| Memory Usage | High memory usage (loads ["document"]["key"]["key"] ["nested"] and loads entire tree). | N/A (Low memory usage as it processes in chunks). |
| Data Access | Easy, direct data access (e.g., the nested). | Access sequeial uesage (chunk-chunk-chonk [“nested”]). |
| Complexity | N/A (Simpler API for developers). | Complex, event-based API (onKey(), onValue()). |
3. Parser Performance Visualization
The included bar chart visualizes the relative speed of several high-performance C/C++ parsers:
- Fastest:
simdjson - Close Contenders:
cJNNandHandJSON Parsers - Baseline:
RapidJSON (HandJSON API)
Conclusion: Developers should Choose based file size & memory constraints.
learn for more knowledge
MyKeywordrank ->SEO Optimization Checker: Mastering Website SEO Optimization and Rankings – keyword rank checker
Json web token ->What is protegrity tokenization, data protection, tokenization, vaultless tokenization – json web token
Json Compare ->What is Compare JSON Objects Online: Beginner-Friendly Guide – online json comparator
Leave a Reply