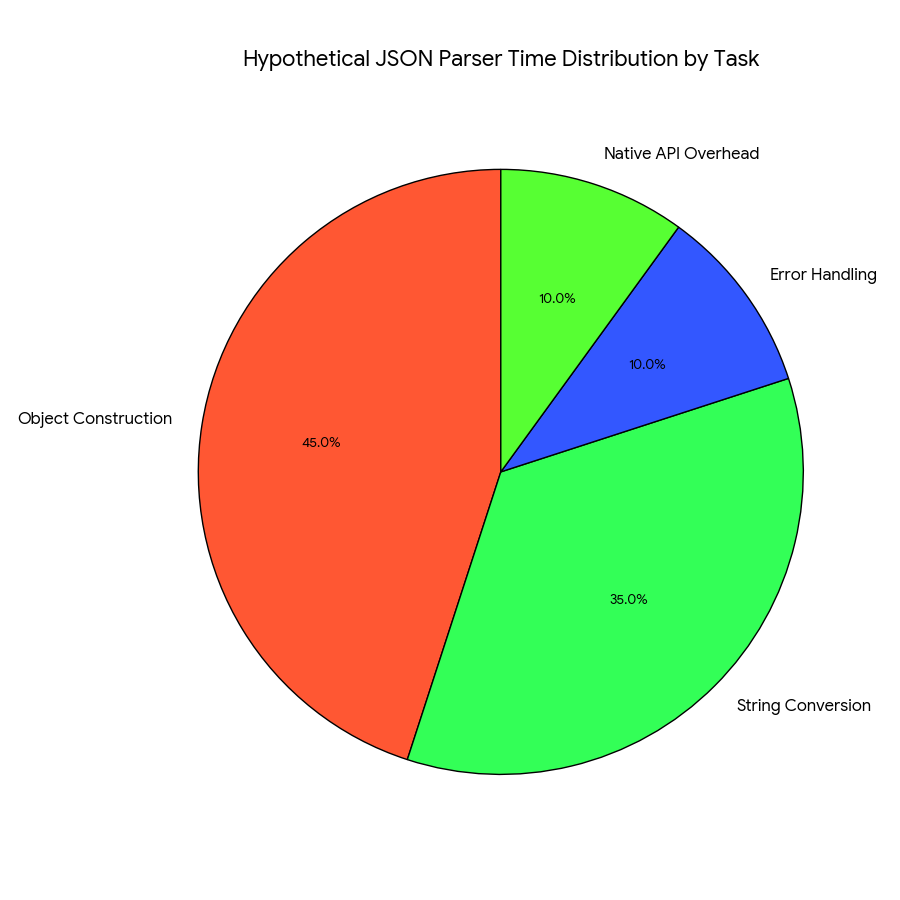
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) has become the de facto standard for data interchange on the web due to its lightweight and human-readable format. Whether you’re working with APIs, configuring applications, or storing data, you’ll inevitably encounter JSON. But raw JSON, especially large files, can be difficult to read and understand without the right tools. This is where a JSON parser comes into play.
What is a JSON Parser?
A JSON parser is a tool or library that takes a JSON string as input and converts it into a native data structure (like objects, arrays, or maps) that can be easily manipulated by a programming language or viewed in a structured, readable format. It helps validate the JSON structure and makes complex data manageable.
Why You Need a JSON Parser
- Readability: Raw JSON can be dense. Parsers pretty-print or tree-view the data, making it easy to navigate.
- Validation: They check if your JSON is syntactically correct, catching errors before they cause issues in your applications.
- Data Extraction: Easily access specific data points within nested JSON structures.
- Efficiency: Automate data processing tasks that would be tedious manually.
Types of JSON Parsers and How to “Download” Them
The term “download” can refer to different methods depending on the type of parser you choose.
1. Programming Language Libraries (Software Dependencies)
For developers, integrating a JSON parser directly into your code is the most common approach. These are typically “downloaded” via package managers rather than direct file downloads.
-
- Python: The built-in
jsonmodule is robust.
- Python: The built-in
import json
json_data = '{"name": "Alice", "age": 30, "city": "New York"}'
parsed_data = json.loads(json_data)
print(parsed_data["name"]) # Output: Alice
-
- Java: Popular libraries include Jackson and Gson. You add them as dependencies in your
pom.xml(Maven) orbuild.gradle(Gradle) file.
- Java: Popular libraries include Jackson and Gson. You add them as dependencies in your
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.13.0</version>
</dependency>
-
- JavaScript: Modern browsers and Node.js have native JSON parsing capabilities.
const jsonString = '{"product": "Laptop", "price": 1200}';
const obj = JSON.parse(jsonString);
console.log(obj.product); // Output: Laptop
-
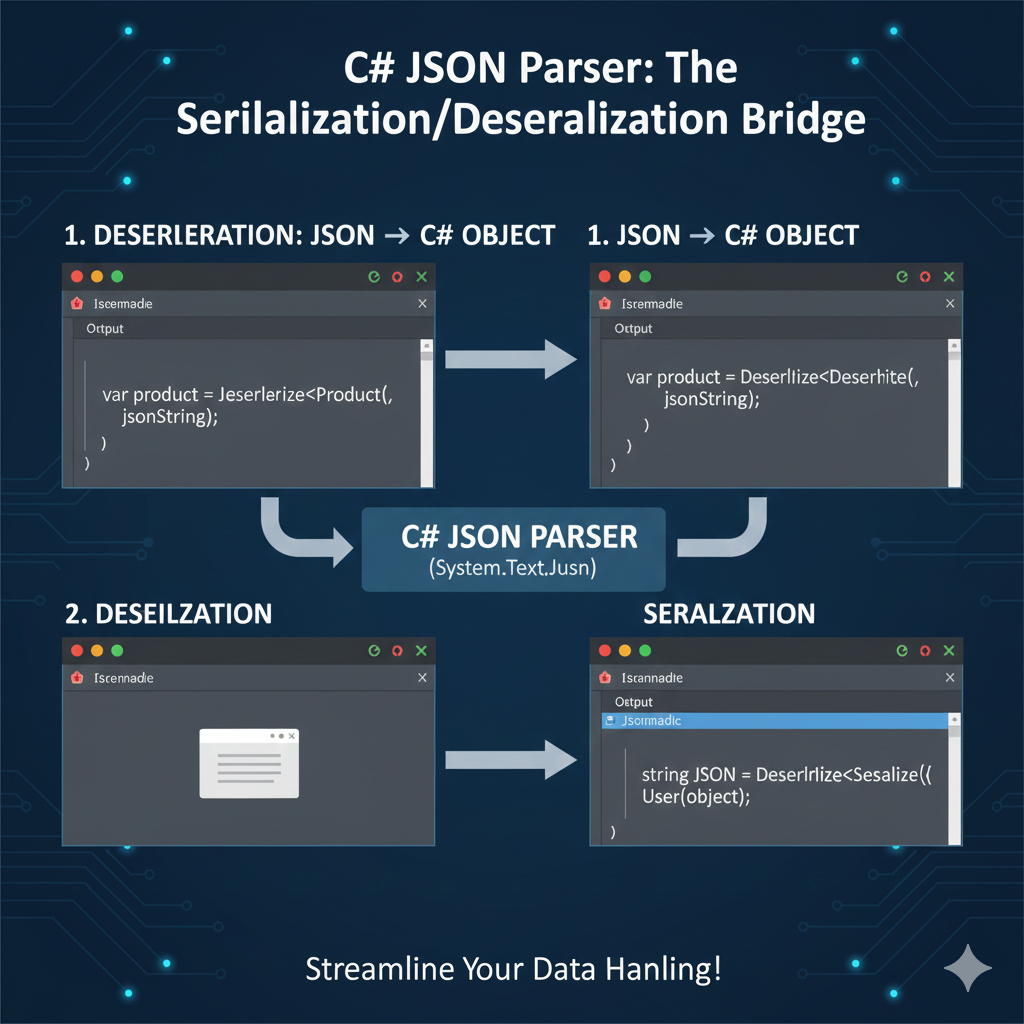
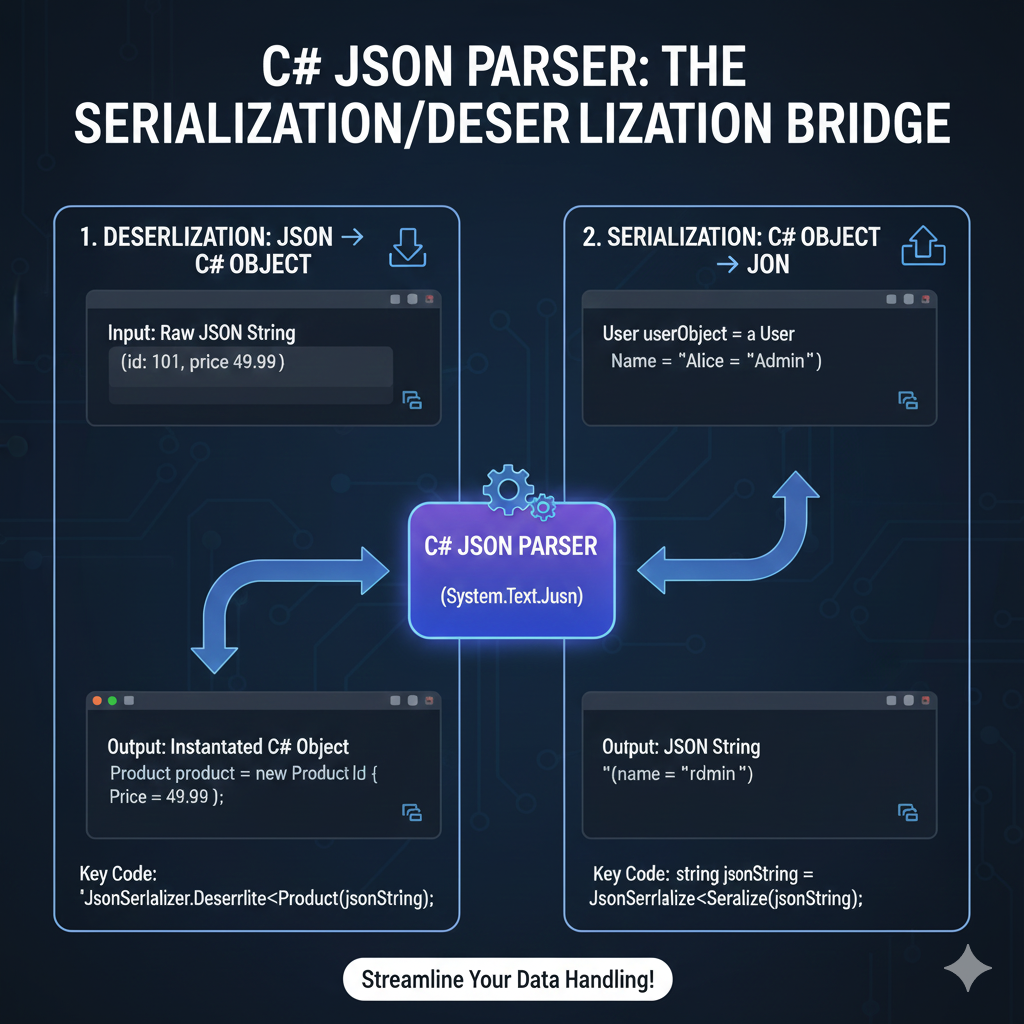
- C#: Newtonsoft.Json (Json.NET) is widely used. Install via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Newtonsoft.Json
2. Online JSON Parsers/Viewers (No Download Required)
If you need to quickly inspect or validate a JSON snippet without writing code, online tools are perfect. You simply paste your JSON, and the tool formats or validates it for you.
- How to Use: Search for “online JSON parser” or “JSON validator” in your browser. Popular options include JSONLint, JSON Formatter & Validator, and various browser extensions.
- Benefits: Instant results, no setup, cross-platform.
- Considerations: For sensitive data, be cautious about pasting it into third-party online tools.
3. Desktop JSON Editors and Viewers (Traditional Download)
For frequent offline work with large JSON files, a dedicated desktop application can offer more features like search, filtering, and advanced editing.
- How to “Download”: Search for “JSON editor desktop app” or “JSON viewer software” for your operating system (Windows, macOS, Linux). Common applications include Visual Studio Code with JSON extensions, Sublime Text with JSON plugins, or dedicated JSON tools like “JSON Editor” by Codebeautify.
- Features to Look For: Syntax highlighting, tree view, search and replace, schema validation, data transformation.
Boosting Your SEO with Properly Parsed JSON
While a JSON parser itself isn’t a direct SEO tool, efficiently handling JSON data indirectly contributes to better SEO:
- Structured Data Implementation: Many SEO best practices involve using JSON-LD for structured data. Parsers help you ensure this data is correctly formatted and validated before deployment, which search engines appreciate.
- API Integration: If your website relies on APIs for content, a robust JSON parsing strategy ensures that dynamic content loads quickly and correctly, improving user experience and page speed – critical ranking factors.
- Error Reduction: Validating JSON with a parser prevents data-related errors that could lead to broken pages or inaccurate information, impacting user trust and search engine crawling.
Conclusion
Whether you’re a developer integrating JSON into an application or a data analyst needing to inspect API responses, knowing how to download and utilize the right JSON parser is crucial. From programming libraries that empower your code to quick online tools and powerful desktop applications, the options are varied and cater to every need. Choose the parser that best fits your workflow to streamline your data handling and indirectly contribute to a more robust, SEO-friendly web presence.
1. What is a JSON Parser & Why You Need One (Bottom Left)
This section defines the core tool and lists its advantages.
- Purpose: A JSON Parser takes complex JSON data (often represented as an array of structured objects, like user records) and converts it into a manipulable format (often native language objects or structs).
- Key Benefits:
- Read Data Manipulable: Allows data to be manipulated and accessed easily.
- Parse Data Manipulable Past Strolls: (Likely intended to mean “Parse Data Manipulated Fast”).
- Work with Faster/Slower when installed: Implies performance benefits when used correctly.
2. Choosing the Right JSON Parser (Top Right)
This section provides a table for comparing different JSON parser options based on key criteria.
| Search | Feature | Performance | Output |
| json | $3.5$ Fast | Romaldi Simplayjozzy | Jozzyt Structure |
| simplgxpn, 38 | $18$ Byte Fast | Runnststx API | Immanie Ftit |
| jjnnsstc; Allst, sgn, 36 | $50$ s Impormnss | Exppand Q Jonnixong | Floorrand Bata Structure |
| Uppsn M/T | $3.$ MIT | Dotcont Eppnssxhis | Kortssffstt |
| License | Dent insstnstns for tsnanssshe jjst jjel | Uiisiorrroe tsr ssse errssed sst posfxannst | Apache $2.0$ |
3. Download the Modern Tech Stack (Bottom Right)
This section diagrams the use of a JSON parser within a typical web service architecture.
- An External API feeds data.
- A Web Server Backend App (or sometimes an Internal Data/Backend App) uses the JSON Parser to ingest data.
- The parsed data is then processed and transformed into User Intended Data before being presented.
4. The Download Process Flow (Top Left)
This flow chart illustrates the steps a system or user takes to download and utilize JSON-related data. The steps are sequential:
- Retrieve Data: System initiates the download.
- Search for Relevant: Search for the appropriate JSON file or data source.
- Process/Parse: The downloaded data is processed by the parser.
- Power-up Data: The structured data is ready to be used.
- Backward Role: (Implied process of integration).
- Analyze and Use: Final step where the clean, parsed data is utilized.
learn for more knowledge
Mykeywordrank ->Search for SEO: The Ultimate Guide to Keyword Research and SEO Site Checkup – keyword rank checker
Json web token ->What Is Okta JWT? (Beginner-Friendly Explanation) – json web token
Json Compare ->Diff JSON Online- The Ultimate Guide to Comparing JSON Files for Developers – online json comparator
Fake Json –>What Is JSON Fake API? (Beginner-Friendly Explanation) – fake api